图像视频基本知识
BMP文件格式解析
由于开源的bmp不能解析使用GDI获得BMP文件,
所以自己使用golang解析BMP文件
1 | type SHORT int16 |
yuv文件
使用RGBA表示一张图像占用的存储空间太大了,人对色调和饱和度不敏感。对亮度敏感。所以色调和饱和度可以压缩更狠。一张图像,转成yuv格式。亮度y的大小为长*宽。u和v长宽只需要一半就行。
即
y = w * h
u = w /2 * h/2
v = w /2 * h/2
FFMPEG使用技巧
FFMPEG编程
接口说明
获得屏幕视频数据流并编码为H264
使用gdigrab可以获得windows下屏幕的数据。
获得摄像头视频数据流并编码为H264
图像工具类demo
读取BMP文件
rgb转yuv
H.264格式
由一个个NALU结构串联结构组成,
由一个一个startCode分割,怎么分割呢?
startCode有0x000001和0x00000001两种,即有三个字节的1为分割点的或4个字节为分割点的1.
startCode为3个字节.[0x00_00_01 {NALU} 0x00_00_01 {NALU} 0x00_00_01{NALU} 0x00_00_01]
找到两个startCode就可以找到一个NALU了。
液晶显示屏彩色显示原理
彩色液晶显示器中,每个像素分成三个单元,或称子像素,附加的滤光片分别标记红色、绿色和蓝色。三个子像素可独立进行控制,通过电压大小来改变亮度,每一个子像素对应8bit,能够产生256颜色。一个像素点能够产生256 * 256 * 256 = 2^24种颜色。
三种原色光在每一象素中以0-255 (28)强度组合成从全黑色到全白色之间各种不同的颜色光,当前在计算机硬件中采取每一象素用24bit(比特)表示的方法,所以三种原色光各分到8比特,每一种原色的强度依照8比特的最高值28分为256个值。用这种方法可以组合16777216种颜色。目前已经存在支持10bit位深的显示器。
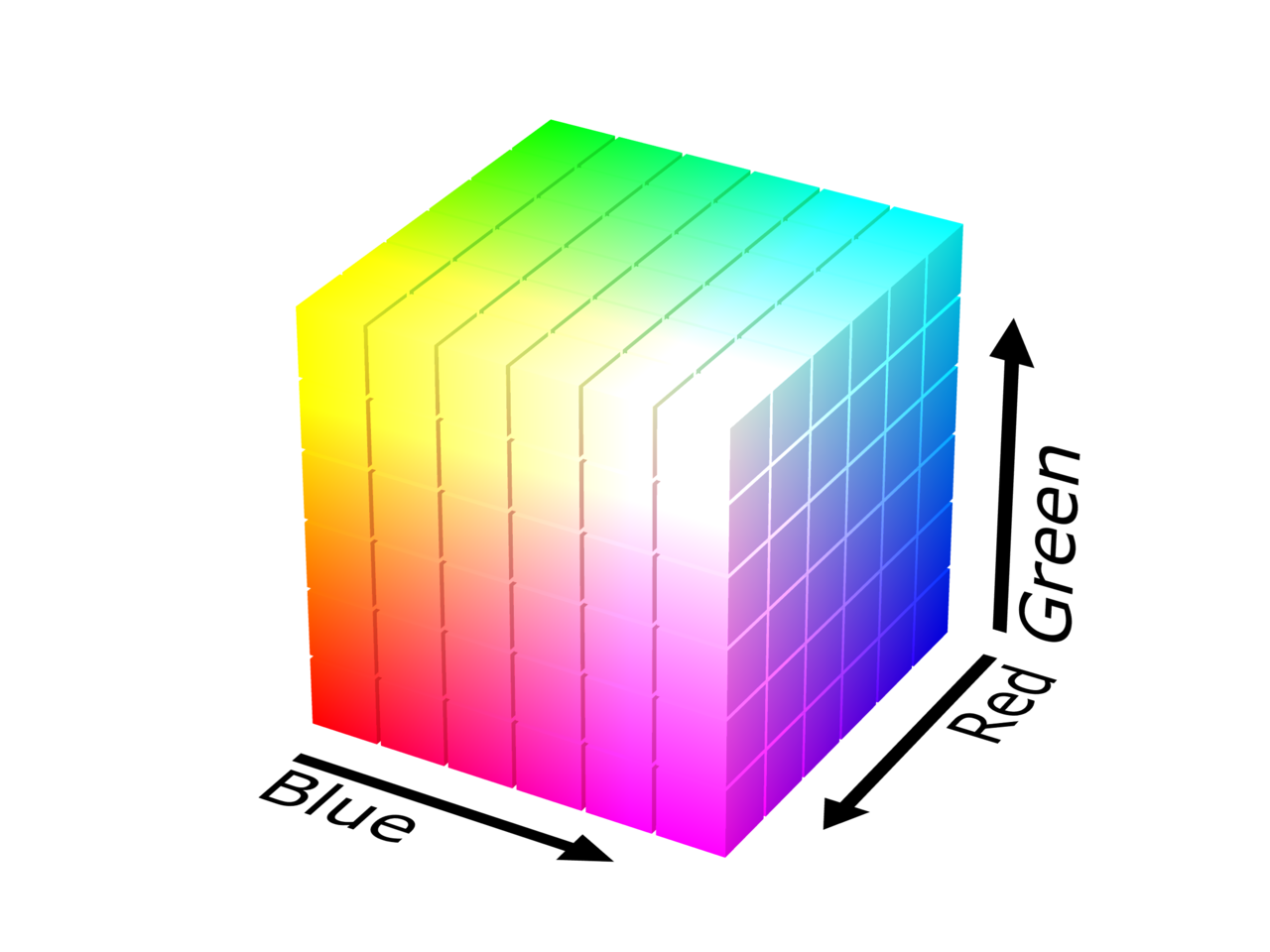
展开:
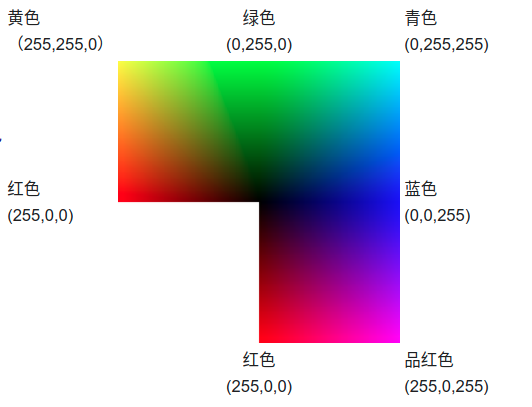
- (0, 0, 0)是黑色
- (255, 255, 255)是白色
- (255, 0, 0)是红色
- (0, 255, 0)是绿色
- (0, 0, 255)是蓝色
- (255, 255, 0)是黄色
- (0, 255, 255)是青色
- (255, 0, 255)是品红
yuv
yuv: 是一种颜色空间,用于彩色电视与黑白电视之间的信号兼容。
- Y: 表明明亮度(Luminance或Luma),灰度图。
- U、V: 表示色度(Chrominance或Chroma), 作用是描述影像的色彩度及饱和度,用于指定像素的颜色。
Y’Cbcr:也称为yuv,
- Cr: 色度红,反应了RGB输入信号 红色部分与RGB信号亮度值之间的差异
- Cb:色度蓝,反应了RGB输入信号 红色部分与RGB信号亮度值之间的差异
yuv存储格式
- planar: 先存储Y,然后U,然后V。
- packed: yuv交叉存储
常见格式
1. yuv444
1 | packet采样(yuv, yuv, yuv)和planar采样(yyyy uuuu vvvv) |
2. yuv422
packet采样,YUYV YUYV或UYVY UYVY
3. yuv422p
planar采样,YYYY UU VV
4. yuv420
1 | packet采样,`YUV Y YUV Y` |
5. yuv420p
1 | planar采样 |
I420: YYYY U V
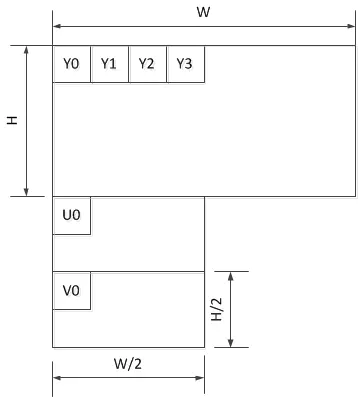
YV12: YYYY V U
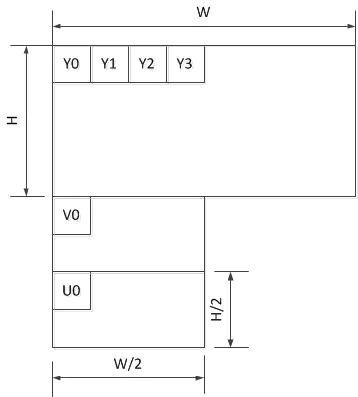
6. yuv420sp
Y为planar采样,UV为paket采样
NV12:
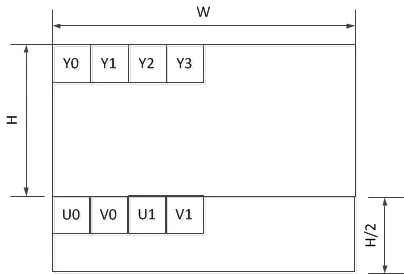
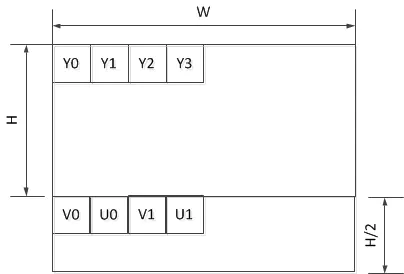
NV21:
RGB
RGBA,每种颜色占一个字节。一个屏幕的像素点由Red、Green、Blue、Alpha组成。
浮点数表示:取值范围[0.0,1.0]
整数表示:取值范围[0,255][0,FF]
格式
1. 索引格式
(1)RGB1
每个像素用1个bit,表示0/1两个值,可表示的范围为两种颜色。黑白;需要使用调色板
(2)RGB4
每个像素用4个bit表示,索引0-15,共16种。
(3)RGB8
每个像素用8个bit表示,可以索引0-255,一共256种颜色。
调色板
一个颜色的索引,一个像素里面的值作为调色板里面索引,该索引对应的调色板的值为对应的颜色值。0/1不一定表示黑白。只表示在调色板中的位置。调色板的值才是表示颜色。
2. 像素格式
(1)RGB555
每个像素用16个bit表示,最高位的bit不用。剩下的15个bit,R、G、B分别占用5个bit。
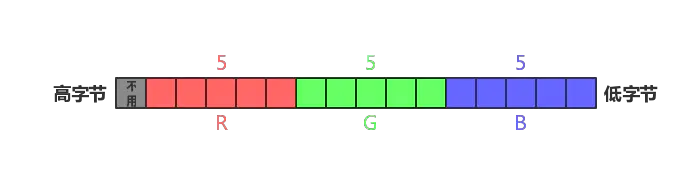
取具体像素值的方法:
- R = color & 0x7C00 // 0x7C00 = 0111_1100_0000_0000
- G = color & 0x03E0 // 0x03E0 = 0000_0011_1110_0000
- B = color & 0x001F // 0x001F = 0000_0000_0001_1111
(2)RGB565
每个像素用16个bit表示,R占用5个、G占用6个、B占用4个。不相等占用。
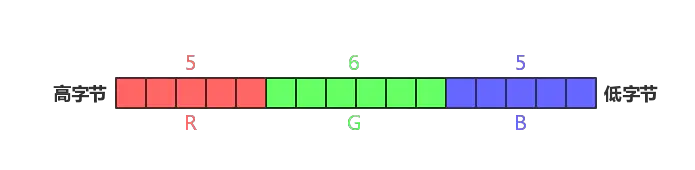
取值的方法:
- R = color & 0xF800(1111_1000_0000_0000)
- G = color & 0x07E0(0000_0111_1110_0000)
- B = color & 0x001F(0000_0000_0001_1111)
(3)RGB24
R、G、B每个用8bit,一共用24bit。
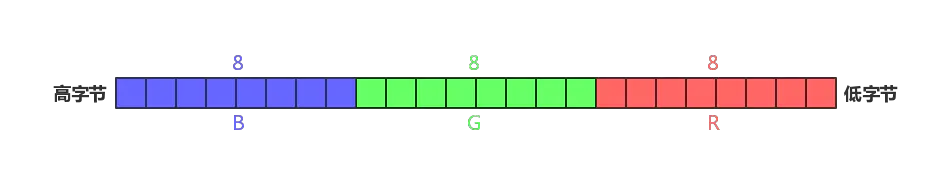
取值计算方法和上面的一样
(4)RGB32
R、G、B每个8bit表示,共占用24bit,最后8个bit保留
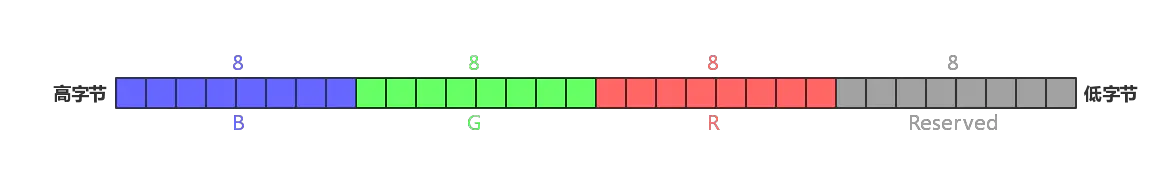
取值计算方法:
- R = color & 0xFF000000
- G = color & 0x00FF0000
- B = color & 0x0000FF00
RGB YUV相互转换
RGB转换成YUV时,U(Cb)、V(Cr)的取值范围整数表示[-128, 127]。浮点数表示[-0.5, 0.5]。
可以统一用一个无符号字节表示[0, 255],对应无符号浮点数[0,1]。有符号和无符号的区别。
YUV -> RGB
1. 常规转换标准
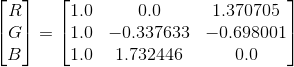
2. BT.601标准 (SD TV)
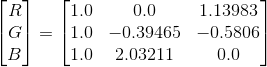
3. BT.709标准 (HD TV)
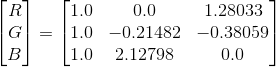
RGB->YUV
1. 常规标准转换
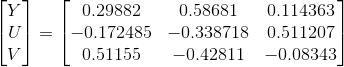
2. BT.601标准:(SD TV)
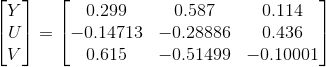
3. BT.709标准: (HD TV)
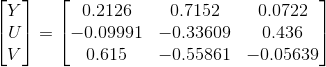
转换Demo
Y’UV444 -> RGB888
用于Y’UV444格式的RGB转换公式也适用于YUV420(或YUV422)的标准NTSC TV传输格式。对于YUV420,由于每个U或V样本都用来表示形成一个正方形的4个Y样本,因此适当的采样方法可以允许使用以下所示的精确转换公式。
这些公式基于NTSC标准:
整数公式:
使用系数:
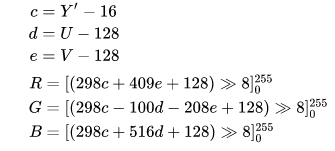
方括号的内容表示:计算出来的值,大于255取255,小于0取,中间值不变。
YCbCr(每通道8位)到RGB888的ITU-R标准整数运算
Y’UV422->RGB888
输入:读取4个字节的Y’UV(u,y1,v,y2)
输出:写入6个字节的RGB(R,G,B,R,G,B)
1 | u = yuv [0]; |
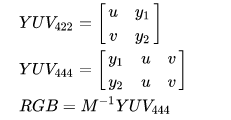
可以将其解析为常规Y’UV444格式以获得2个RGB像素信息:
1 | rgb1 = Y'UV444toRGB888(y1,u,v); |
Y’UV422也可以用其他顺序的值表示,例如FourCC格式代码YUY2。
输入:读取4个字节的Y’UV(y1,u,y2,v),(y1,y2,u,v)或(u,v,y1,y2)
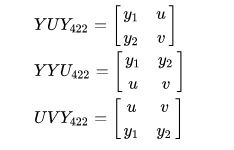
Y’UV411->RGB888
输入:读取6个字节的Y’UV
输出:写入12个字节的RGB
1 | //提取YUV分量 |
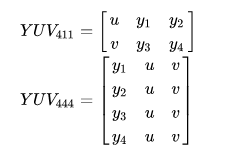
我们从6个字节中获得了4个RGB像素值(4 * 3字节)。这意味着将传输的数据的大小减小一半,而质量下降。
Y’UV420p和(Y’V12或YV12)->RGB888
Y’UV420p是平面格式,这意味着Y’,U和V值被分组在一起而不是散布在一起。这样做的原因是,通过将U和V值分组在一起,图像变得更加可压缩。当给定Y’UV420p格式的图像数组时,所有Y’值首先出现,然后是所有U值,最后是所有V值。
Y’V12格式基本上与Y’UV420p相同,但是它切换了U和V数据:Y’值后跟V值,最后是U值。只要注意从适当的位置提取U和V值,就可以使用相同的算法处理Y’UV420p和Y’V12。
与大多数Y’UV格式一样,Y’值与像素一样多。在X等于高度乘以宽度的情况下,数组中的前X个索引是对应于每个单独像素的Y’值。但是,U和V值只有四分之一。U和V值对应于图像的每个2×2块,这意味着每个U和V条目都适用于四个像素。在Y’值之后,下一个X / 4索引是每个2 x 2块的U值,此后的下一个X / 4索引是V值,它们也适用于每个2 x 2块。
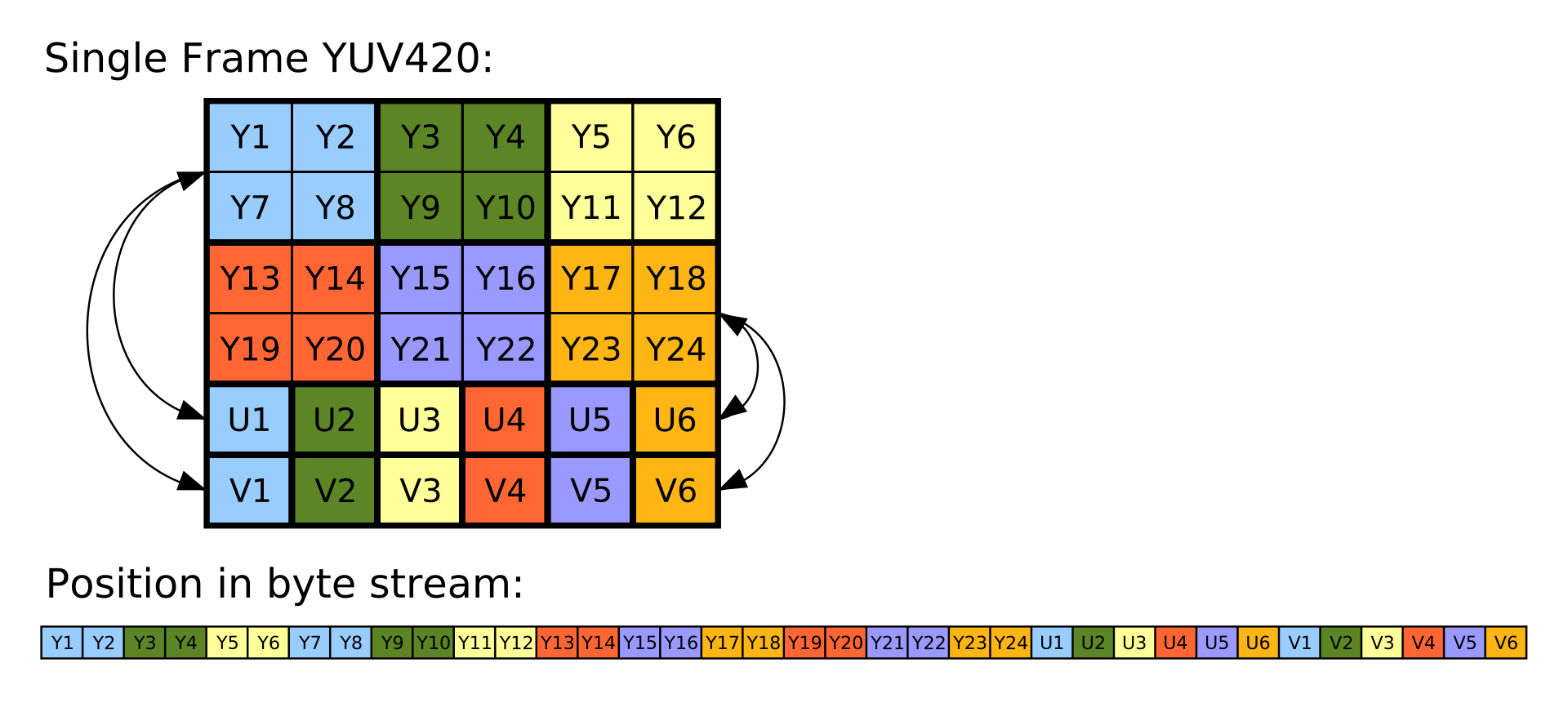
如上图所示,Y’UV420中的Y’,U和V分量分别在顺序块中编码。为每个像素存储AY’值,然后为每个2×2正方形像素块存储一个U值,最后为每个2×2块存储一个V值。在上图中,使用相同的颜色显示了相应的Y’,U和V值。从设备逐行读取字节流,Y’块位于位置0,U块位于位置x×y(在此示例中为6×4 = 24),V块位于位置x ×y +(x×y)/ 4(这里6×4 +(6×4)/ 4 = 30)
参考
(1) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/YUV
H.264相关
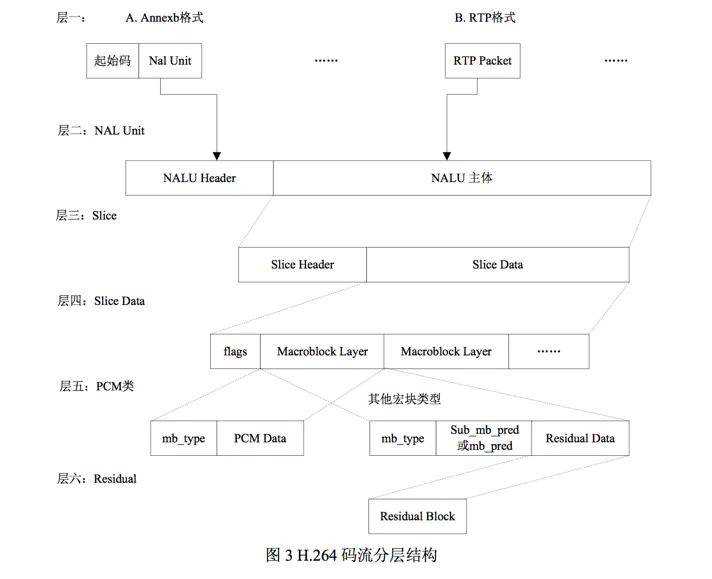
NALU
H.264原始码流,由一个一个NALU组成。

它的功能分为两层:视频编码层(VCL, Video Coding Layer),和网络提取层(NAL, Network Abstraction Layer)。
VCL数据编码处理的输出,输出的是原始数据比特流(SODB,String of Data bits),被压缩编码后的视频数据序列,真正的二进制码流,但是大小和长度不一定。在传输存储前需要字节对齐,即往原始数据后面添加字节。生成原始字节序列负荷(RBSP, Raw Byte Sequence Payload)。最后被封装到NAL单元中(NALU, NAL Unit)。
每个NALU包括:
- 一组对应于视频编码的NALU头部信息。这个里面是什么信息????
- 一个原始字节序列负荷(RBSP, Raw Byte Sequence Payload)。RBSP在原始编码数据(SODB)后面填充bit,一个“1”bit和若干个”0”。用来字节对齐。每个NALU大小一定符合特定的格式。

NALU作为一个独立的单元,只要完整的传送NALU便可以播放了。
Start Code
如何将NALU分割开来,需要一个一个起止码(Start Code Prefix)进行分割。如果NALU对应的Slice为一帧的开始,首帧。使用4字节表示,即0x00 00 00 01。不是首帧或其他数据类型,使用3字节表示0x00 00 01。为了保证起始码唯一,当数据连续出现0x00 00 00、0x00 00 01、0x00 00 02、0x00 00 03时,会在两个0之间插入03。保证只有起止码唯一。
1 | 0x00 00 00 -> 0x00 00 03 00 |
NAL Header
1byte的NAL Header头格式,forbidden_bit(1bit) + nal_refence_bit(2bit) + nal_unit_type(5bit)
- forbidden_bit(1bit)禁止位,有语法冲突,设为1。接收方识别之后需要丢弃这个NALU
- nal_ref_idc(2 bit)当前NAL的优先级,取值为0~3,值越高表明当前NAL越重要。H.264规定,如果当前NAL是序列参数集,或是图像参数等。该值必须大于0.nal_unit_type为5,nal_ref_idc > 0; nal_unit_type ={6,9,10,11,12}时,nal_ref_idc等于0。
- nal_unit_type(5 bit)类型如下。
| nal_unit_type | NAL类型C | C |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 未使用 | |
| 1 | 未使用Data Partitioning、非IDR图像的Slice | 2,3,4 |
| 2 | 使用Data Partitioning、且为Slice A | 2 |
| 3 | 使用Data Partitioning、且为Slice B | 3 |
| 4 | 使用Data Partitioning、且为Slice C | 4 |
| 5 | IDR图像中的Slice | 2,3 |
| 6 | 补充增强信息单元(SEI) | 5 |
| 7 | 序列参数集(Sequence Parameter Set,SPS) | 0 |
| 8 | 图像参数集(Picture Parameter Set,PPS) | 1 |
| 9 | 分界符 | 6 |
| 10 | 序列结束 | 7 |
| 11 | 码流结束 | 8 |
| 12 | 填充 | 9 |
| 13…23 | 保留 | |
| 24…31 | 未使用 |
nal_unit_type=5时,表示当前NAL是IDR图像的一个片,此时,IDR图像中的每个片的nal_unit_type都应该等于5。
1 | RBSP = SODB+ RBSP trailing bits |
H.264有两种封装模式:
(1)annexb模式:传统模式,有start code, SPS和PPS是在ES中;
(2)mp4模式:没有start code,SPS和PPS是封装在container中,每一个frame前面是这个frame的长度;
SPS的头部是0x67,PPS的头部是0x68,要保持对数据的敏感性。
判断能否都丢帧的依据是,根据NALU包的优先级字节,如果优先级为0,则可以丢弃,如果是IDR、SPS、PPS时,优先级会大于0。
- SPS:Sequence Parameter Set 序列参数集,H.264码流第一个 NALU
- PPS:Picture Parameter Set图像参数集,H.264码流第二个 NALU
- IDR帧:IDR帧属于I 帧。解码器收到IDR frame时,将所有的参考帧队列丢弃 ,这点是所有I帧共有的特性,但是收到IDR帧时,解码器另外需要做的工作就是:把所有的PPS和SPS参数进行更新。由此可见,在编码器端,每发一个 IDR,就相应地发一个 PPS & SPS_nal_unit
- I帧:帧内编码帧是一种自带全部信息的独立帧,无需参考其它图像便可独立进行解码,视频序列中的第一个帧始终都是I帧。
- P帧:前向预测编码帧
- B帧:双向预测内插编码帧
一般H.264原始码流是以SPS->PPS->SEI->IDR->SLICE->SLICE…开头的。
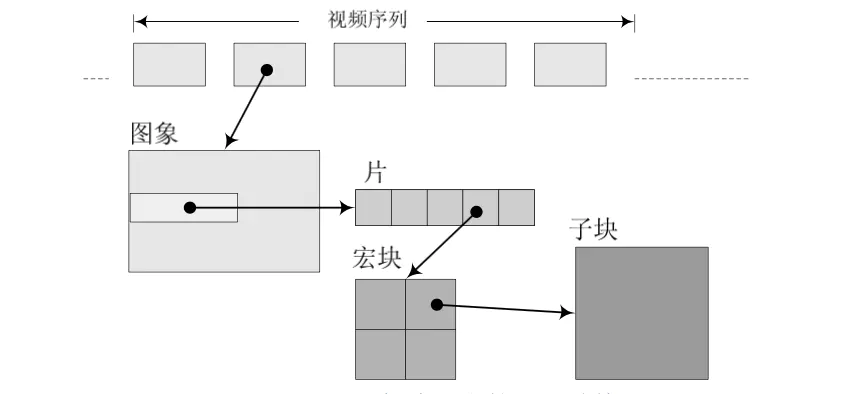
一帧图片数据和NALU的关系
一帧图片被编码之后,编成一个或多个片(slice)。大卸八块了??使用NALU来装载Slice。但是NALU不只装Slice。slice一定用NALU装,NALU不一定装的是slice。
1 | graph LR |
帧和片的概念:一帧一定是一张完整的图片。就像拼图一样,一个拼图一定是一张图片,但是拼图会分成一块一块的。那小块的就是片。
slice
一个片又是由什么组成的???片头+片数据。
片头都有那些数据???
片数据由什么组成???
片数据由一个一个宏块组成,至少有一个宏块。宏块是什么?
宏块包含每一个像素的亮度和色度信息,解码的工作就是从宏块中获得像素数据阵列数据。一个宏块包含:宏块类型+预测类型+CPB(Coded Block Pattern)+QP(Quantization Parameter)+宏块数据
宏块数据: 16 × 16的亮度像素 + 8 × 8的Cb +8 × 8的Cr组成。每一个宏块都是长宽为16的YUV420P的数据??? 可以选其他的数据吗??
切片的类型:
- 0 P-slice. Consists of P-macroblocks (each macro block is predicted using one reference frame) and / or I-macroblocks.
- 1 B-slice. Consists of B-macroblocks (each macroblock is predicted using one or two reference frames) and / or I-macroblocks.
- 2 I-slice. Contains only I-macroblocks. Each macroblock is predicted from previously coded blocks of the same slice.
- 3 SP-slice. Consists of P and / or I-macroblocks and lets you switch between encoded streams.
- 4 SI-slice. It consists of a special type of SI-macroblocks and lets you switch between encoded streams.
整体结构
一个视频编码之后生成一组又一组的图像(GOP,图像组)。每个GOP形容一个I帧到下一个I帧之间间隔了多少帧。间隔越大,视频体积越小,视频的质量越低。如何理解?假设一个视频的帧率为25f,说明一秒内需要播放25帧的数据。如果只有一个I帧,其余的都是P帧或B帧,那么数据量会很小。如果25帧都是I帧,那就相当于每秒钟播放完整的25张图片。那数据就很大。如何描述一个GOP的参数,图像多少,帧间隔多少,长宽多少,帧率多少。需要传输中的序列(PPS)和帧图像参数(SPS)
雷神音视频博客笔记
音视频数据处理入门:RGB、YUV像素数据处理
1 |
|
视音频数据处理入门: H.264视频码流解析
H.264原始码流(又称为“裸流”)是由一个一个的NALU组成的。他们的结构如下图所示。

每个NALU之间通过startcode进行分隔
1 | startcode NALU startcode NALU startcode NALU |
startcode有两种0x000001(3byte)和0x00000001(4byte)。两个起始码可以分隔出NALU。
NALU Header
NALU头部固定为2个字节。结构和占用的大小如下
1 | nal_unit_header { |
解析DEMO
1 | typedef enum { |
FFMPEG使用命令
使用ffmpeg提取视频关键帧
ffmpeg -i video.m4s -vf select='eq(pic_type\,I)' -vsync 2 -f image2 core-%02d.jpeg
从MP4文件中提取H264
ffmpeg -i ./2153.mp4 -codec copy -bsf: h264_mp4toannexb -f h264 tmp.264
列出windows系统输入输出设备
ffmpeg -list_devices true -f dshow -i dummy
结果:
1 | [dshow @ 00000296de63df00] DirectShow video devices (some may be both video and audio devices) |
读取摄像头的数据
使用上一个步骤生成的结果ffplay -f dshow -i video="Chicony USB2.0 Camera"
除了使用dshow之外,还可以使用vfwcap播放摄像头数据ffplay -f vfwcap -i 0
查看设备选项,使用list_options选项ffmpeg -list_options true -f dshow -i video="Chicony USB2.0 Camera"
输出
1 | [dshow @ 0000026aed70e080] DirectShow video device options (from video devices) |
跟据这些选项设置摄像头输出参数
设置摄像头分辨率
ffplay -s 320x240 -f dshow -i video="Chicony USB2.0 Camera"摄像头数据编码成H.264,发布UDP
ffmpeg -f dshow -i video="Chicony USB2.0 Camera" -vcodec libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency -f h264 udp://localhost:6666
使用-preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency提高编码速度。编码为H.264,发布RTP
ffmpeg -f dshow -i video="Chicony USB2.0 Camera" -vcodec libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency rtp rtp://localhost:6666 > test.sdp
推流的同时生成sdp文件摄像头编码为H.264,发布RTMP
ffmpeg -f dshow -i video="Chicony USB2.0 Camera" -vcodec libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency -f flv rtmp://xxxxx.xxx.xx编码为MPEG2,发布UDP
ffmpeg -f dshow -i video="Chicony USB2.0 Camera" -vcodec mpeg2video -f mpeg2video udp://localhost:6666播放MPEG2的UDP流
ffplay -vcodec mpeg2video udp://localhost:6666
读取屏幕数据
简单的录制
ffmpeg -f gdigrab -i desktop out.mpg从屏幕的(10,20)点处开始,抓取640x480的屏幕,设定帧率为5
ffmpeg -f gdigrab -framerate 5 -offset_x 10 -offset_y 20 -video_size 640x480 -i desktop out.mpg将屏幕录制后编码成H.264文件
ffmpeg -f gdigrab -i desktop -r 5 -vcodec libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency Desktop.mkv-r 5表示帧率为5屏幕录制的时候加上话筒声音
ffmpeg -f gdigrab -i desktop -f dshow -i audio="麦克风 (Realtek High Definition Audio)" -r 5 -vcodec libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency -acodec libmp3lame MyDesktop.mkv屏幕送流和摄像头送流类似
ffmpeg -f gdigrab -i desktop -r 5 -vcodec mpeg2video -f mpeg2video udp://localhost:6666抓取屏幕特定窗口
ffmpeg -f gdigrab -i title="C:\WINDOWS\system32\cmd.exe" -r 5 -vcodec libx264 -preset:v ultrafast -tune:v zerolatency Desktop.mkv
使用上述的方法生成H264流无法正常传送,需要重新设置sps,pps和编码的格式,才顺利的在手机端播放。得先转成yuv,再使用yuv编成h264,这样就可以顺利的使用mediacodec进行编码。